In the ever-evolving field of welding, understanding welding bead types is critical for achieving high-quality welds. With advancements in technology, tools like augmented reality (AR) welding simulators have revolutionized how welders learn and practice these techniques. In this article, we will explore the different types of welding beads, their applications, and how AR-based training enhances learning and performance.
What is a welding bead?
A welding bead is the result of a welder’s movement as they join two materials together. It is the visible, physical evidence of the welding process and serves as a hallmark of skill and precision. Beads come in various types, shapes, and sizes, each tailored for specific tasks and materials.
Types of welding beads
|
Welding bead |
Description | Applications |
Advantages |
|
1. Stringer Bead |
A stringer bead is a straight, narrow line of weld created by moving the welding torch or electrode in a linear motion. | This type is ideal for thin materials and where precision is paramount. Stringer beads are often used in root passes and when welding in tight spaces. | Simple to execute and produces clean, narrow welds with minimal spatter. |
|
2. Weave Bead |
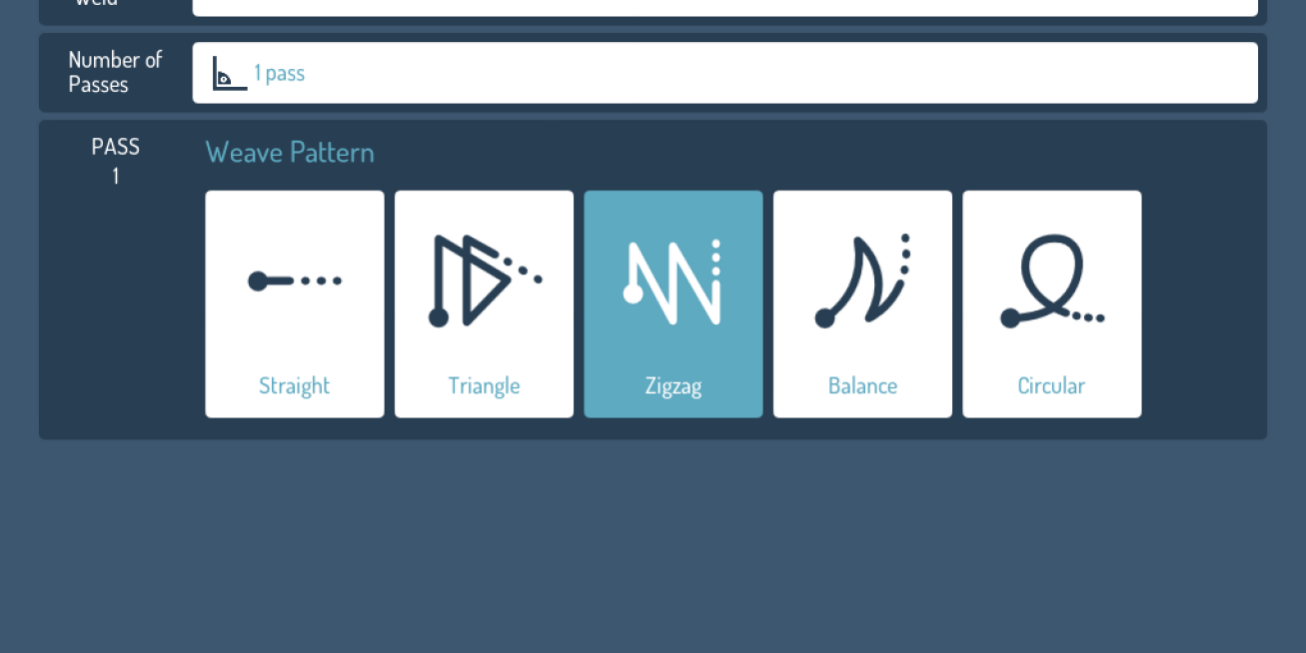
A weave bead involves a side-to-side motion of the torch or electrode, creating a wider and more substantial weld. | Perfect for filling larger gaps or when working with thicker materials. It is commonly used in multi-pass welds and for structural welding. | Provides better penetration and coverage, ensuring a stronger joint. |
|
3. Circular or Spiral Bead |
As the name suggests, this bead is formed using a circular or spiral motion, creating a distinct texture and shape. | Used for specific finishes or to weld in situations where circular motion enhances joint strength. | Allows for even distribution of heat and filler material. |
|
4. Whip Bead |
Created by a forward-and-back motion, whip beads are particularly effective in controlling heat. | Common in welding thin materials to avoid burn-through and when working with materials prone to warping. | Provides excellent control over penetration and bead shape. |
|
5. Stacked Dime Bead |
Recognized by its aesthetically pleasing, rippled appearance, the stacked dime bead mimics a row of overlapping coins. | Typically associated with TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding for its precision and clean look, often used in automotive and artistic applications. | Offers strong welds with a visually appealing finish. |
Choosing the right welding bead for your project
When deciding which bead type to use, consider factors such as:
- Material Thickness: Thicker materials often require weave beads for better coverage, while thin materials work well with stringer beads.
- Joint Type: For open gaps, weave beads may be necessary, while root passes often need stringer beads.
- Position: Welding in vertical or overhead positions may influence the choice of bead and technique.
The role of Augmented Reality in learning welding beads
Understanding bead types is one thing, but mastering them requires practice. Traditionally, welding training relied heavily on physical equipment and materials. However, augmented reality (AR) welding simulators are changing the scene.
|
Benefits of AR Welding Simulators |
|
|
Risk-Free Environment |
Trainees can practice different welding bead techniques without the risk of burns or injuries. |
|
Visualization |
Trainees can visualize bead profiles and learn to correct inconsistencies, reinforcing theoretical knowledge with hands-on application. |
|
Immediate Feedback |
Simulators provide real-time feedback on parameters like speed, angle, and distance, helping learners improve faster. |
|
Repetition and Skill Building |
Users can repeatedly practice techniques, ensuring muscle memory and precision. |
| Cost-Effective |
AR reduces material waste, saving on metals, gases, and other consumables. |
With Soldamatic, welders can simulate creating stringer beads, weave beads, and more in various scenarios and positions. This AR technology prepares them for real-world challenges with unparalleled efficiency.
The welding simulator mimics real welding processes, including TIG, GTAW, and other methods, with detailed visualizations of bead geometry and material behavior. Soldamatic also incorporates a Learning Management System (LMS) for course customization and progress tracking.
This AR welding solution allows trainees to practice in a risk-free environment, helping them build confidence before handling live equipment. Soldamatic also provides real-time feedback, video replays, 3D views, and parameter analysis to improve their performance. Furthermore, it represents a paradigm shift in vocational training, offering an environmentally sustainable and highly effective alternative to traditional methods. Its global adoption underscores its success in addressing the skills gap in the welding industry.
As a conclusion, Soldamatic has been tailored for vocational training and industry-specific requirements, helping institutions adapt to the Industry 4.0.
Mastering welding bead types
With innovations like augmented reality welding simulators, trainees can gain hands-on experience in a controlled, immersive environment; mastering their welding knowledge and becoming a skilled welder.
Whether you are working on structural projects, pipelines, or artistic designs, understanding and applying the right welding bead type will ensure strong, durable, and visually appealing welds.
Seabery’s cutting-edge AR welding simulators provide the perfect platform for learning these skills, bridging the gap between theory and practice. As technology continues to shape the future of welding, investing in advanced training tools will empower the next generation of welders to excel in their craft.