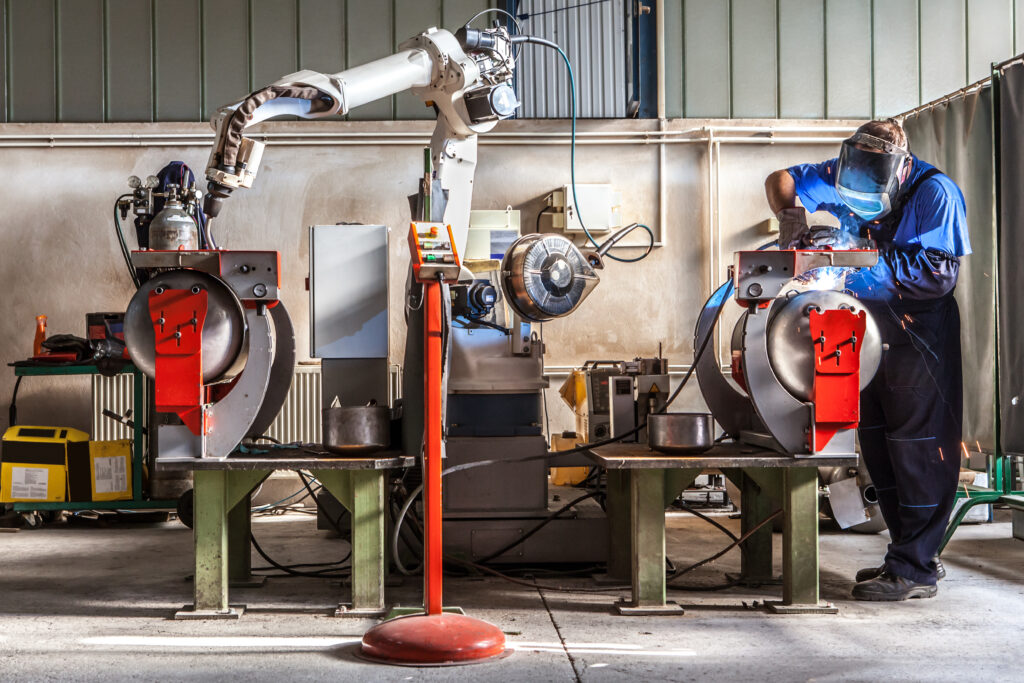
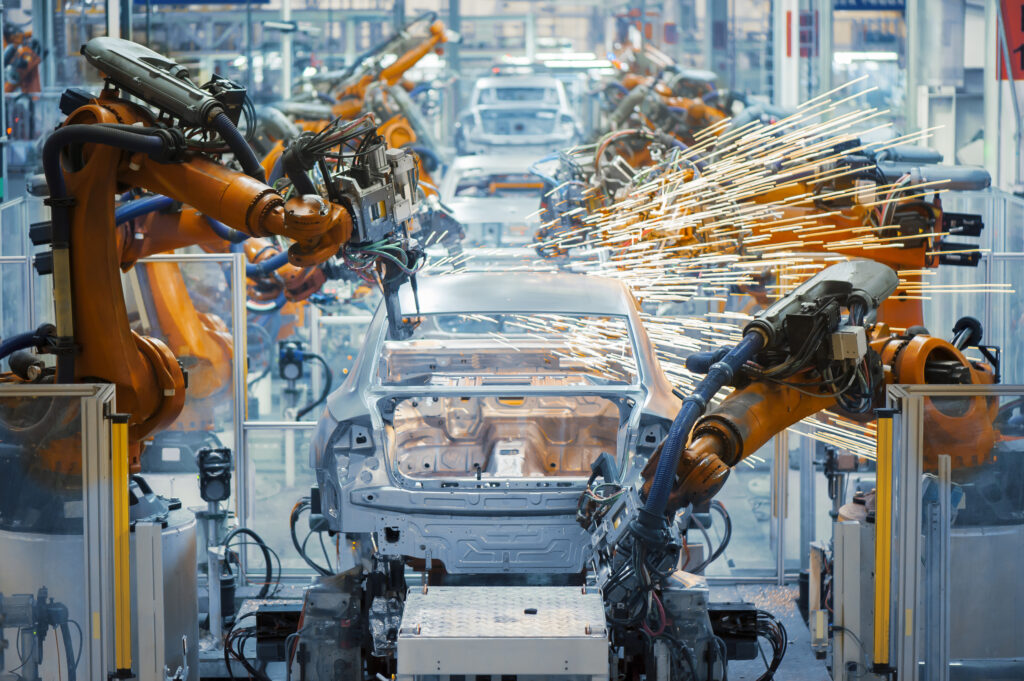
The industrial sector is undergoing a profound transformation driven by automation and digitalization. Manufacturing environments are becoming increasingly connected, data-driven, and efficiency-focused. In this context, welding has evolved from a manual craft into a highly technological discipline.
Companies are integrating robotics, artificial intelligence, and advanced simulation tools to improve quality, reduce costs, and address the growing shortage of skilled welders. As production cycles become shorter and quality standards stricter, automated welding solutions are playing a key role in boosting productivity and ensuring consistent results. This article delves how welding automation is no longer a futuristic concept but a strategic necessity.
What is welding automation?
Welding automation refers to the use of mechanized systems, robotics, and digital technologies to perform welding tasks with minimal human intervention. Unlike manual welding, automated systems follow pre-programmed parameters to ensure precise and repeatable results.
Organizations such as the American Welding Society (AWS) define welding automation as systems that improve repeatability, quality, and safety by minimizing human variability.
There are different levels of automation:
- Mechanized welding: Equipment assists the welder but requires human control.
- Semi-automatic welding: The welder controls the process, but filler material feed and parameters are automated.
- Fully automated and robotic welding: Industrial robots perform the welding process with limited operator supervision.
Why welding automation is essential for productivity
1. Increased production speed
Automated welding systems operate at consistent speeds without fatigue. Unlike manual welding, robots can work continuously, significantly increasing throughput. According to the International Federation of Robotics, industrial robot installations continue to grow worldwide, particularly in sectors where welding represents a significant production bottleneck.
2. Improved consistency and quality
In industries such as aerospace and oil & gas, weld defects can lead to severe safety and financial consequences. Automated systems ensure consistent heat input, travel speed, and torch positioning, reducing rework and scrap rates.
3. Reduced labor dependency
The global shortage of qualified welders is a growing challenge. The American Welding Society has repeatedly warned about a significant skills gap in the welding workforce. Automation helps companies maintain productivity even when skilled labor is limited, while experienced professionals can focus on supervision and quality control.
4. Enhanced workplace safety
Automation reduces exposure to hazardous fumes, extreme temperatures, and repetitive strain injuries. Robotic welding cells isolate dangerous operations, contributing to safer industrial environments.
Welding automation across industrial sectors
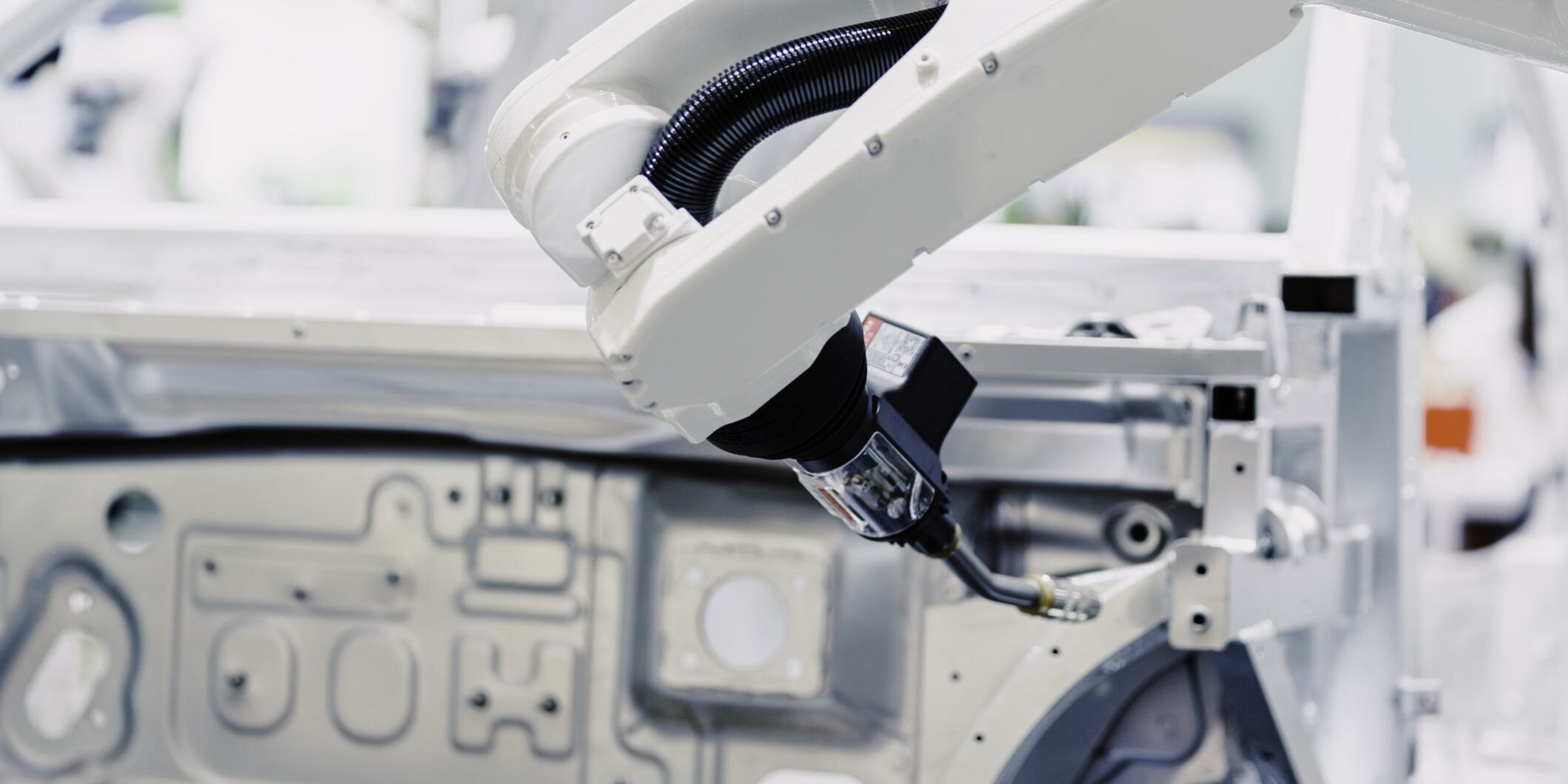
| Automotive | The automotive sector has long been a pioneer in robotic welding. High production volumes and repetitive tasks make automation essential for maintaining profitability and quality standards. |
| Aerospace and Aviation | Aerospace welding requires extreme precision and traceability. Automated systems ensure compliance with strict certification standards and documentation requirements. |
| Oil & Gas | Pipeline construction and pressure vessel manufacturing benefit from orbital and automated welding systems that ensure high-quality welds in critical applications. |
| Railway and Shipbuilding | Large-scale structures demand consistent weld quality across long seams. Automation reduces distortion and improves structural integrity. |
Technologies driving welding automation
Industrial Robotics: Robotic welding systems integrate articulated arms, advanced sensors, and adaptive controls. Major automation providers such as ABB, FANUC, and COMAU have developed specialized welding robots capable of high-precision operations.
Industrial IoT and Data Analytics: Smart welding machines collect real-time data on voltage, current, wire feed speed, and arc stability. These metrics feed into analytics platforms, enabling predictive maintenance and process optimization which are key elements of digitalization strategies in Industry 4.0.
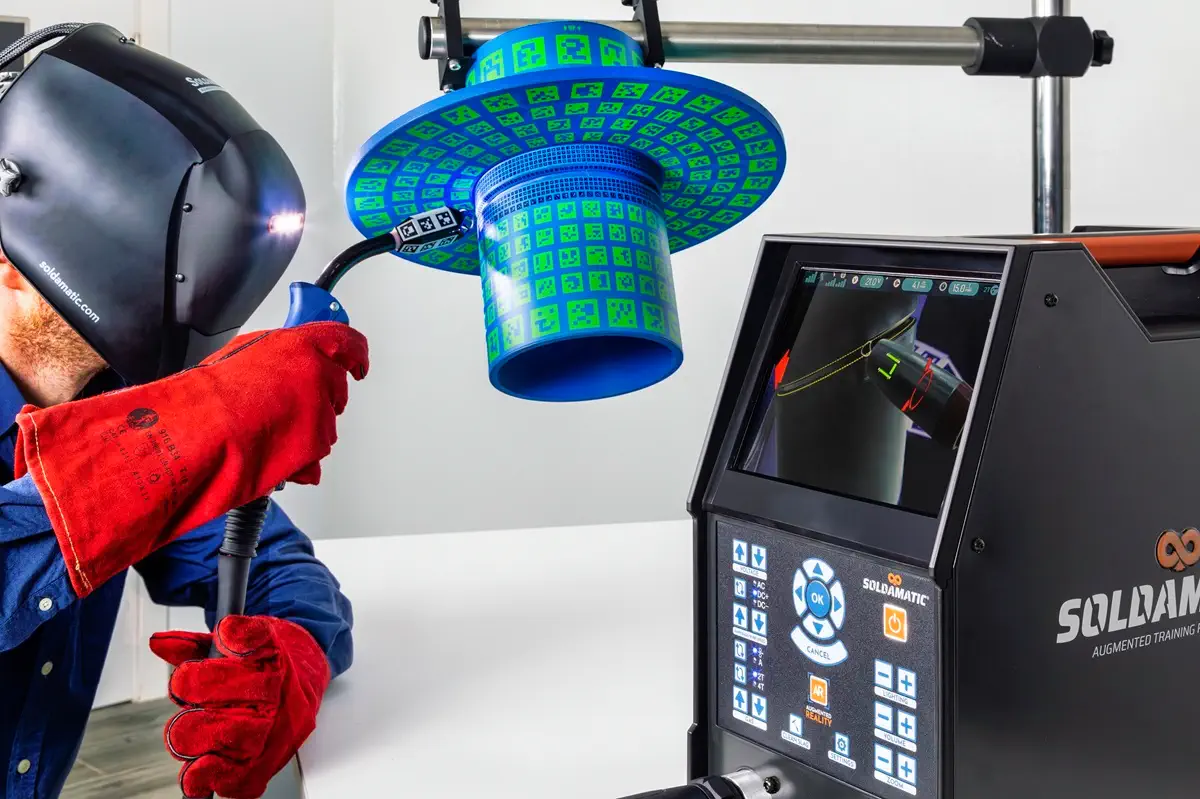
Augmented Reality and Simulation: Augmented Reality is increasingly used in welding training and process validation. By overlaying digital information onto real-world environments, AR systems improve methodology, training efficiency, and skill acquisition before operators work with actual automated cells.
Digital Twin Technology: Digital twins allow manufacturers to simulate welding processes before physical execution. By creating a virtual model of the weld joint and parameters, companies can optimize cycle time and reduce errors.
Workforce transformation
While automation increases productivity, it does not eliminate the need for skilled professionals. Instead, it transforms the welding methodology. Modern welders must understand:
· Robotic programming.
· Process parameter optimization.
· Quality inspection standards.
· Data interpretation and analytics.
Training methodologies must evolve accordingly. Educational institutions and industrial training centers are incorporating digital tools and welding simulators to prepare operators for automated environments.
In a context where automation and digitalization are reshaping the welding industry, training solutions must also evolve. This is where Augmented Reality and advanced simulation systems play a crucial role. By practicing in safe, controlled environments, trainees develop both manual and automated welding competencies aligned with industrial demands.
Seabery Welding Simulator provides an innovative approach to preparing professionals for automated industrial environments. Unlike traditional training methods, Seabery’s solution allows users to:
· Practice welding techniques in a fully immersive and measurable environment.
· Analyze real-time performance data.
· Develop process understanding aligned with industrial automation standards.
· Reduce material consumption and operational costs.
By integrating objective performance metrics and digital feedback, the welding simulator bridges the gap between traditional craftsmanship and automated production lines. It supports institutions and industrial companies in developing a workforce capable of operating, supervising, and optimizing automated welding systems. This methodology aligns perfectly with Industry 4.0 strategies, where automation, data analytics, and digitalization converge to enhance productivity and quality.
Automation as a competitive advantage
Welding automation is not simply about replacing manual labor with machines. It is about improving methodology, increasing productivity, enhancing safety, and enabling data-driven decision-making.
As industrial sectors continue their digital transformation, companies that adopt automated welding systems and invest in advanced training solutions will gain a decisive competitive advantage. Productivity, quality, and sustainability are no longer optional: they are fundamental requirements in modern manufacturing.
Automation, digitalization, and Augmented Reality are shaping the future of welding. Organizations that combine robotic systems with advanced training methodologies will be best positioned to meet the demands of tomorrow’s industrial landscape.
Would you like to book a free online demo?
If you are interested in experiencing first-hand the power of Seabery Welding PRO, we invite you to complete our form to request a personalized demo – contact us now to explore the possibilities Seabery can offer your company or training center!