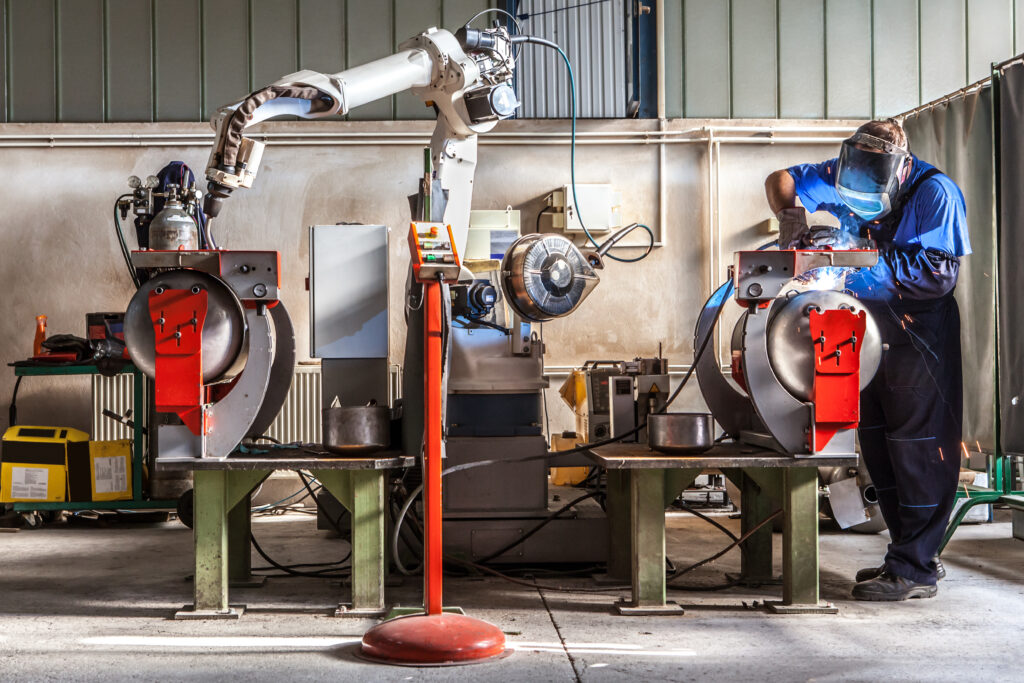
Organisations increasingly demand operators who not only weld manually, but also programme, operate and maintain robotic cells. In this article we explore Robotic Welding Training Programs, diving into their methodology and why they are becoming indispensable in industrial welding.
What are robotic welding training programs?
Robotic welding training programs are structured educational pathways designed to equip welders, technicians and engineers with the skills to work with automated welding systems: typically robotic arms, cell controllers, sensors and associated automation. These programs cover topics like robot programming, welding process set-up, safety, system integration, and quality assurance.
For instance, the American Welding Society (AWS) offers its “Certified Robotic Arc Welding (CRAW)” certification which confirms a person’s ability to programme and execute a robot weld according to industry standards.
Training for a welding robot operator includes instruction and hands-on work: system basics, programming, safety, and hands-on with robots. Without training, you might find robotic systems hard to use, causing mistakes and delays.
|
Key components and methodology of robotic welding training |
|
|
Theoretical modules |
Covering automation fundamentals, robot kinematics, welding metallurgy, safety in robotic cells. For example, a programme may begin with robotics and automation basics. |
|
Programming and operations |
Using teach pendants, setting tool frames, user frames, adjusting weld schedules, troubleshooting. One training provider’s syllabus: create tool/user frames, write arc-weld programs, use macros. |
|
Hands-on practice |
Actual robotic welding systems or simulation/cell environments. Practice on live robots or in a training cell helps contextualise theory. |
|
Safety and integration |
Vital given the risks of robotic welding. Training includes safety rules, robot cell hazards, emergency stop, etc. |
|
Assessment and certification |
Verifying competence via tests or practical exams, often aligned with industry standards. AWS CRAW is an example. |
Methodology for industrial applications
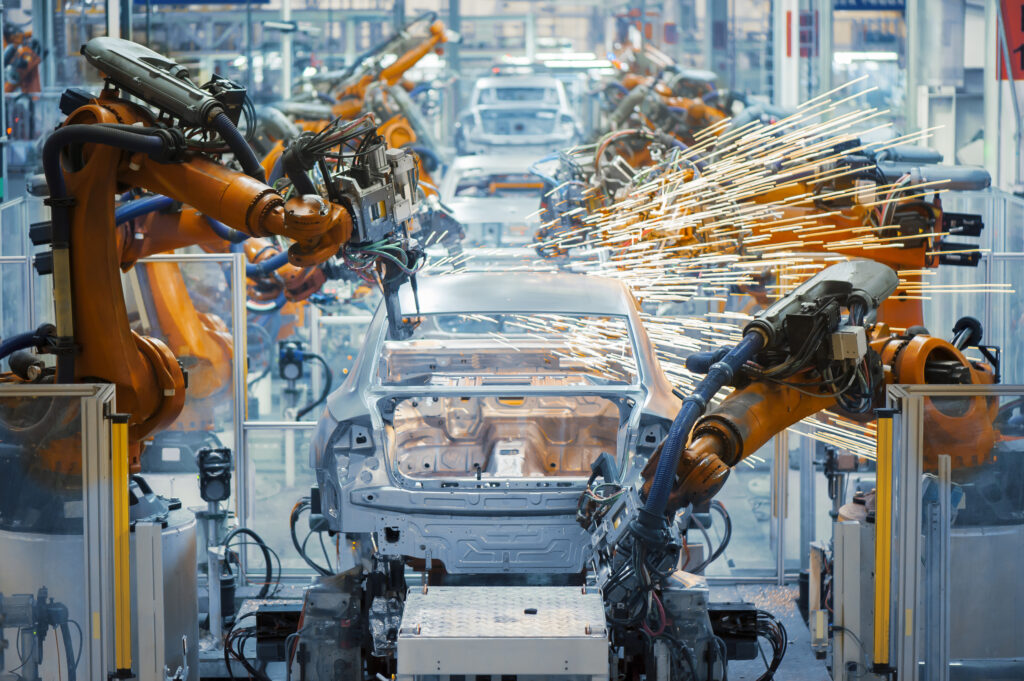
Training is key to making industrial automation successful. In an industrial context, these training programs are often customised to the company’s specific robotic welding set-up, welding processes, materials, fixtures, and production goals.
Seabery designs and delivers AR robotic welding training tailored to each client’s automation setup, the skill level of their workforce, and their specific operational objectives and timelines; ensuring that every program maximizes both learning efficiency and production performance. This ensures that training is not generic, but deeply relevant to the automation environment of the workshop.
Why this matters: industrial automation and digitalization
As manufacturers adopt robotic welding cells (for higher speed, less waste, improved quality, among other advantages), the workforce must evolve. Without trained staff, the investment in automation cannot reach full potential.
Furthermore, the role of the Robotic Welding Technician is increasingly demanding for programming, integration, monitoring, and quality assurance.
Role of simulation in robotics welding training
Digital tools such as welding simulators and virtual training platforms are becoming core enablers of modern robotic welding training programs.
- Reduced risk: trainees can practice without live arc and fumes.
- Customized learning: simulation allows adjusting difficulty, materials, processes, at the learner’s pace.
- Better engagement: AR/VR environments improve retention, accelerate learning curves, and enable safe practice.
- Cost minimization: fewer consumables (wire, gas, samples), less waste, less setup cost.
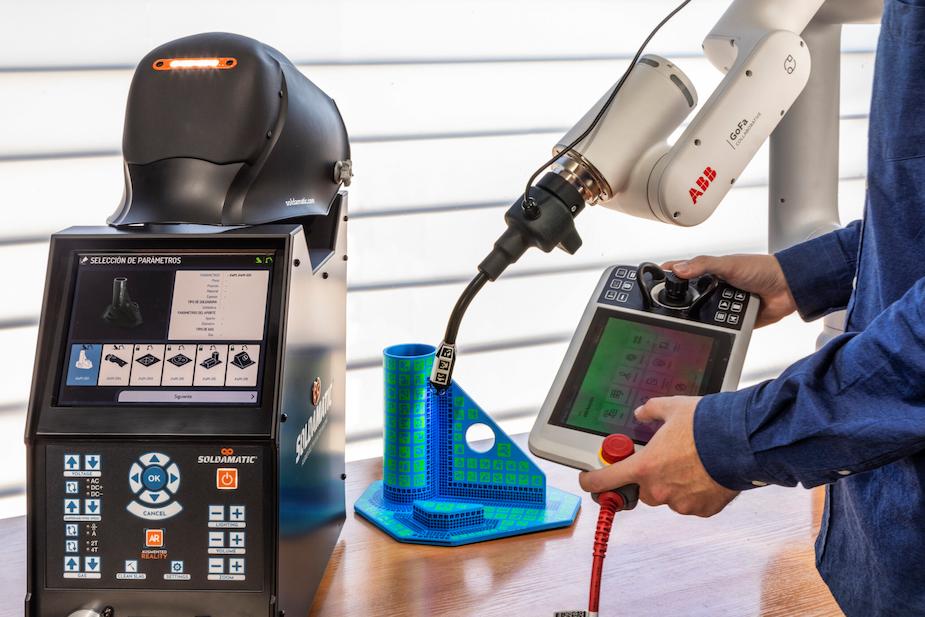

| How this integrates in robotic welding training |
| Introduce robotic cell programming and operation in a virtual or augmented lab before live robot use. |
| Allow learners to test program changes, path corrections, welding parameters, without tying up production equipment. |
| Provide remote or off-site training modules, supporting digitalisation of training delivery. |
| Feed data into learning analytics systems, supporting adaptive training and tracking performance. |
As organizations look to digitalize training, reduce downtime, and scale workforce skills across multiple sites or geographies, these methods align well with the broader shift to Industry 4.0.
Integrating Seabery’s solution into robotic welding training
Seabery Robotics Welding Simulator supports this new paradigm. This solution is described as:
· A realistic, complete and flexible training system for robotic welding.
· Using Augmented Reality, working with real components.
· Integratable with any robot on the market, and designed to train operators in robot programming for specific welding routines.
For instructors and companies looking to implement robotic welding training programs, Seabery’s approach offers the technical infrastructure (AR and real robot interface) required to bridge the gap between theory and live operation. Furthermore, this welding simulator fits neatly into the methodology and needs described earlier for robotic welding training programs.
Operators can learn programming, tool frames, user frames and welding process scheduling in a virtual environment before touching live production machines. This means that training occurs in a safe, controlled environment, reducing risk, consumable waste and learning time.
The system supports scaling training across multiple units or remote locations, aligning with digitalization efforts. This approach strengthens an industrial organization’s automation strategy, combining a skilled workforce, digital training, and robotic welding cells to achieve higher quality, greater efficiency, and reduced downtime.
| Seabery Robotics: Advanced welding joints applicable | |
| AWM009 | Robotic Foundational “House” |
| AWM010 | Robotic Foundational “Face” |
| AWM015 | Robotic Foundational Assembly |
| AWM016 | Robotics Foundational Complex Sequence |
| AWM017 | Robotics Foundational Ability Test |
| AWM018 | Robotics Foundational “Chinese Character – 大” |
| AWM019 | Robotics AWS CRAW |
Empowering automation through education
In summary, robotic welding training programmes are a critical component of modern manufacturing, enabling companies to maximize the value of their automation investments. Topics such as robot programming, process integration, safety, and digital training methods are central. The synergy between workforce development and digitalization cannot be ignored.
With Seabery’s AR-based robotic welding training solution, organizations can embrace this next generation of training, reducing risk, improving skill acquisition, and aligning with Industry 4.0 objectives.