The welding industry is undergoing a profound transformation driven by digitalization, automation, and the increasing demand for highly skilled professionals. Traditional welding training methods—based on consumables, physical workshops, and instructor-dependent evaluation—are no longer sufficient to meet modern industrial and educational requirements. In this context, Augmented Reality welding simulators have emerged as a powerful methodology to improve training quality, safety, and efficiency.
However, not all welding simulators are the same. Choosing the right solution requires a clear understanding of technical, pedagogical, and industrial criteria. This article explores how to choose a welding simulator, focusing on key aspects such as learning methodology, industrial applicability, data analytics, and long-term value.
Define the training objectives

Before comparing technologies, it is essential to define why you need a welding simulator. Different organizations have different goals:
- Training centers and vocational schools focus on teaching fundamentals, certification preparation, and reducing material costs.
- Industrial companies aim to upskill workers, standardize processes, reduce defects, and support automation strategies.
- Corporate academies often need scalable, repeatable training aligned with internal quality standards.
A good welding simulator must align with your methodology, whether introductory training, advanced process optimization, or continuous improvement programs. Without clear objectives, even the most advanced simulator may fail to deliver value.
Augmented Reality vs. Virtual Reality
One of the first decisions is choosing between Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) simulators.
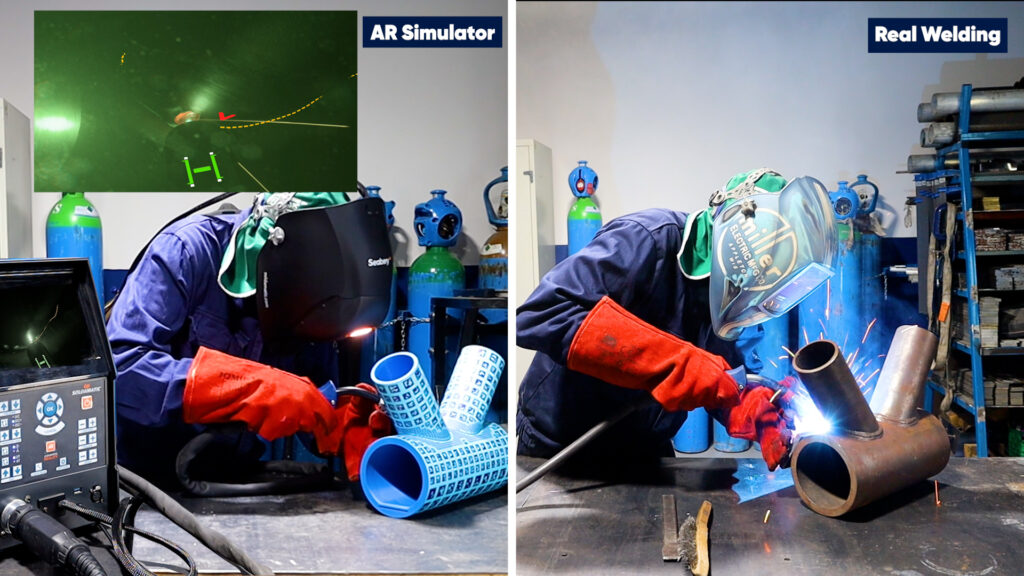
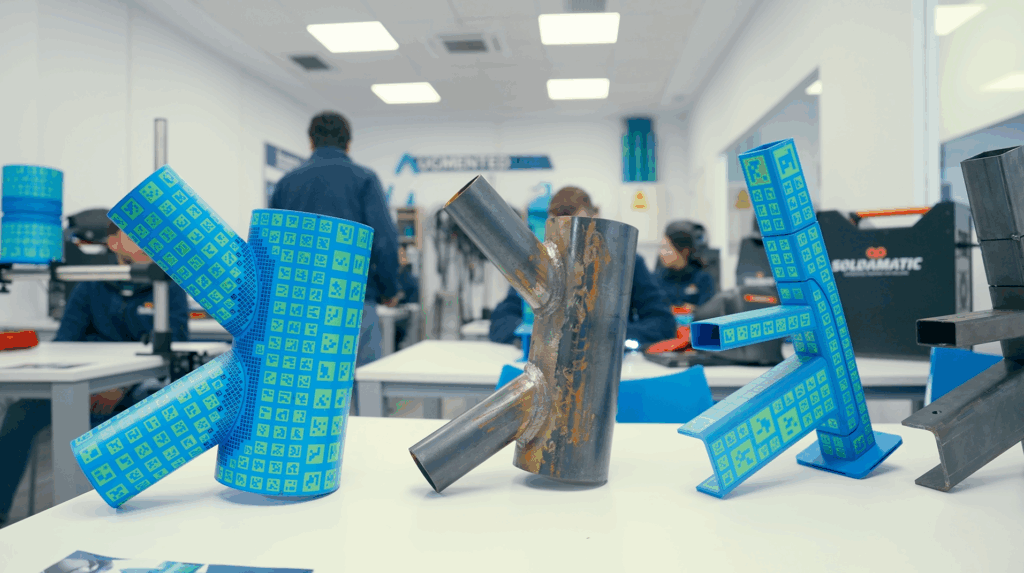
Augmented Reality welding simulators integrate real physical components (such as torches, helmets, and workpieces) with digital overlays. This allows trainees to develop real motor skills, correct posture, and realistic hand-eye coordination.
Virtual Reality simulators, on the other hand, offer fully digital environments. While useful for visualization and basic concepts, they often lack the tactile realism required for industrial-grade welding training.
For organizations focused on industrial readiness and certification, AR is generally the preferred methodology.
Welding processes and industrial relevance
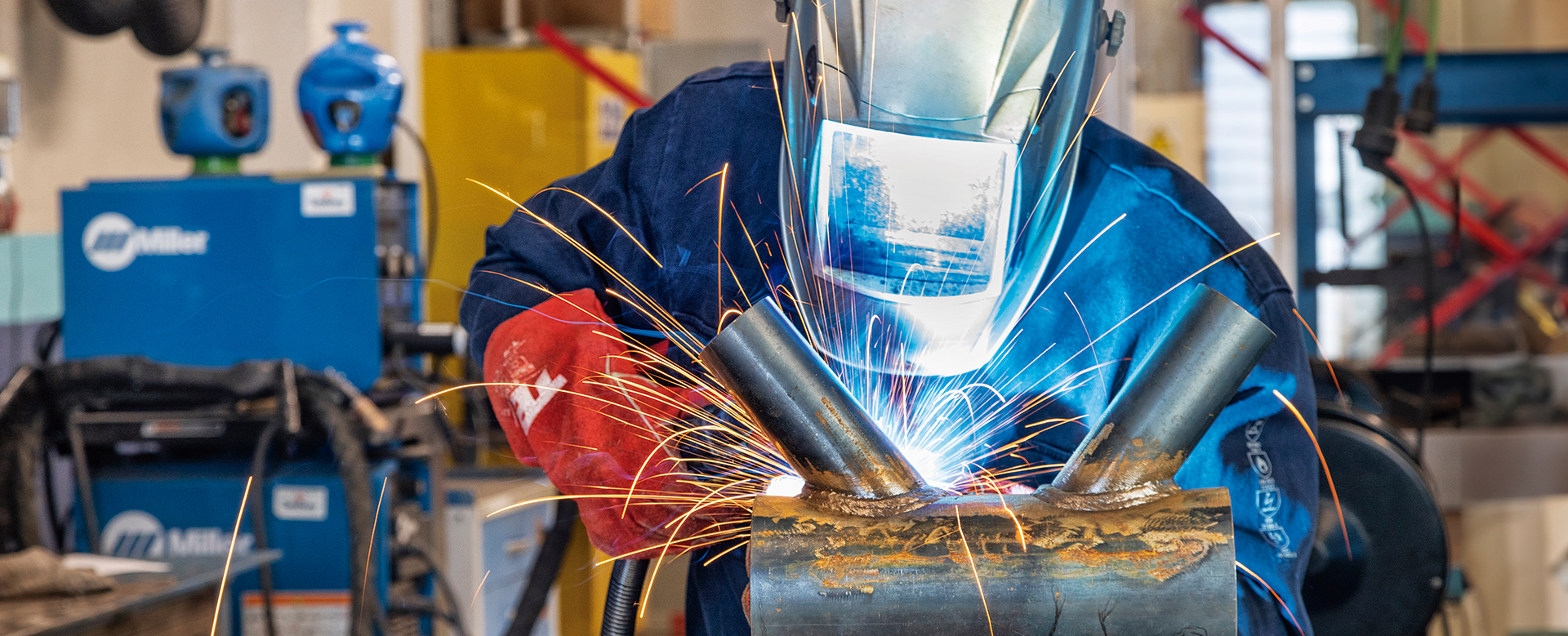
Another critical factor is the range of welding processes supported by the simulator. A high-quality solution should cover (at least) MIG/MAG, TIG, and MMA (Stick welding).
Additionally, the simulator should allow configuration of industrial parameters such as voltage, amperage, wire speed, and shielding gas. This ensures alignment with real industrial welding procedures and standards.
Industrial relevance is especially important for companies operating in sectors such as automotive, aerospace, shipbuilding, railways, and oil & gas, where precision and repeatability are essential.
Learning methodology and feedback system
A welding simulator is not just a machine; it is a training methodology. Look for solutions that provide:
- Real-time feedback on torch angle, speed, distance, and position.
- Objective scoring systems based on standardized criteria.
- Progressive learning paths, from beginner to advanced levels.
- Instructor tools for monitoring and evaluation.
The ability to translate performance into measurable data is a key advantage of digital training. Simulators that integrate analytics help instructors identify skill gaps and personalize training programs.
Data, digitalization, and analytics
In the era of Industry 4.0, data is a strategic asset. Modern welding simulators should support:
- Individual performance tracking.
- Historical data comparison.
- Exportable reports.
- Integration with Learning Management Systems (LMS).
This level of digitalization transforms welding training from a subjective process into a data-driven system. For industrial environments, this also enables alignment with quality management systems and continuous improvement initiatives.
Safety, sustainability, and cost efficiency
One of the strongest arguments for welding simulators is their impact on safety and sustainability. Key benefits include:
- Zero exposure to fumes, heat, and electrical risks during training.
- Elimination of material waste (metal plates, electrodes, gas).
- Significant reduction in energy consumption.
- Lower long-term operational costs.
From an ESG perspective, simulators contribute directly to more sustainable industrial training models, while also reducing the total cost of ownership for training centers and companies.
Scalability and ease of implementation
When choosing a welding simulator, consider not only current needs but also future growth. Important questions to ask:
- Can the system be easily updated with new modules?
- Does it support multiple users and locations?
- Is it suitable for both educational and industrial environments?
- How intuitive is it for instructors and trainees?
A scalable solution ensures long-term value and adaptability as training requirements evolve due to automation and new industrial standards.
Turning welding training into a data-driven process
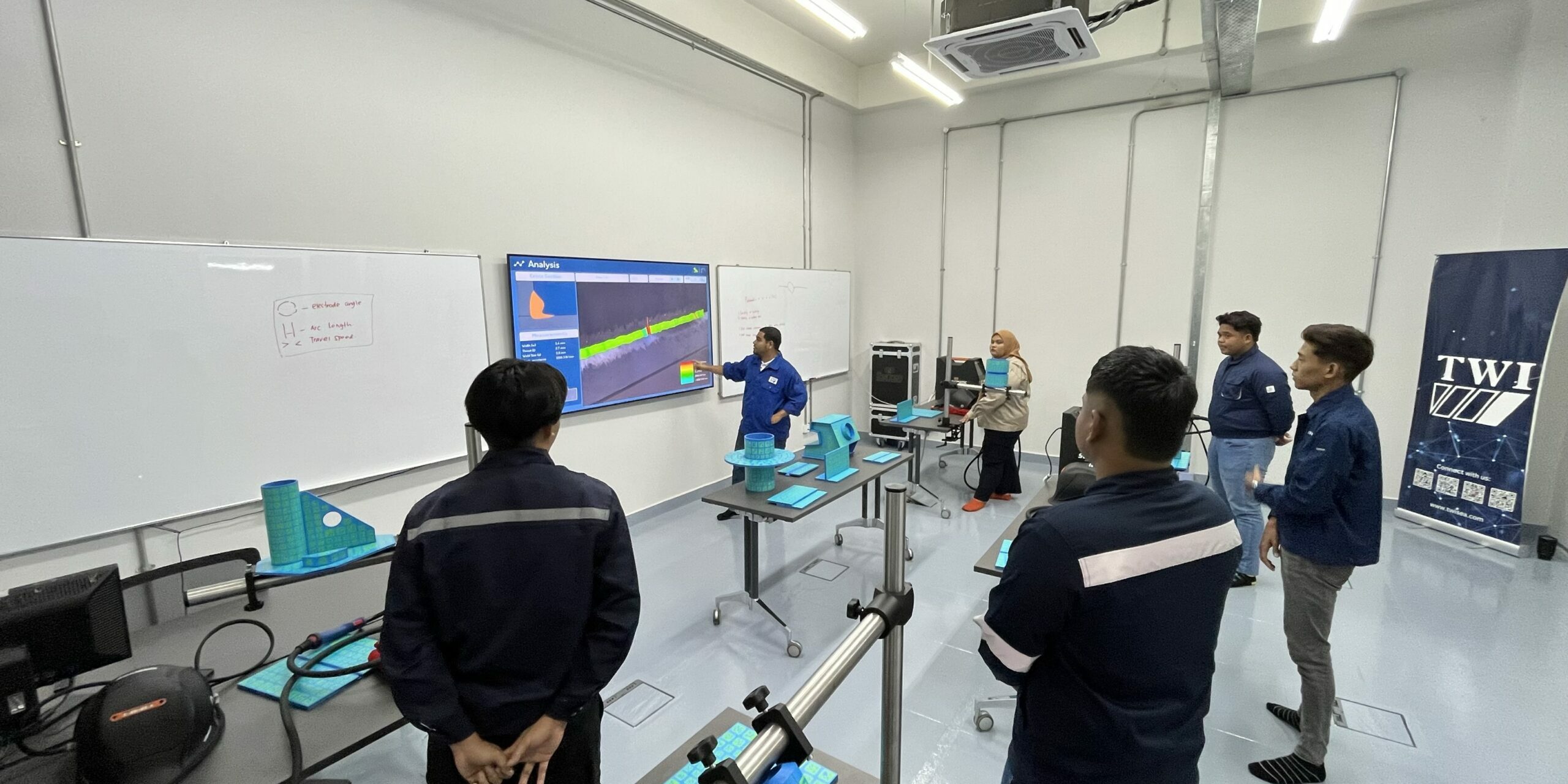
When evaluating how to choose a welding simulator, Seabery’s solution represents a benchmark in Augmented Reality welding training.
Seabery Welding Simulator is structured to support progressive learning paths, allowing trainees to move from basic motor skills to advanced industrial techniques in a controlled environment. This methodology helps instructors spend less time correcting fundamental mistakes and more time coaching advanced skills. As a result, learning curves are shorter, pass rates for certifications improve, and training programs become more efficient and scalable.
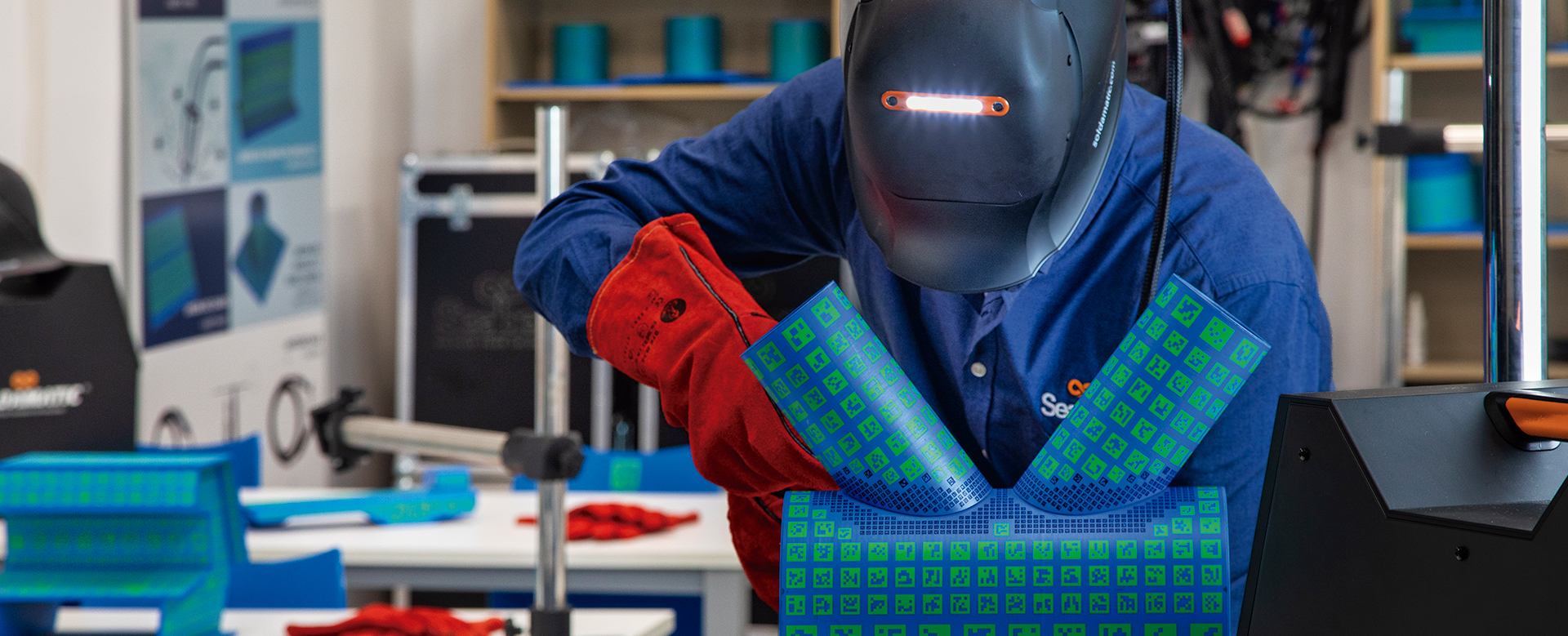


This welding simulator is also designed to meet the demands of industrial welding training, where consistency, repeatability, and quality control are critical. By digitizing welding parameters and performance metrics, industrial organizations can align training with internal procedures, reduce variability between operators, and support continuous improvement initiatives linked to automation and quality assurance systems.
It allows trainees to develop essential skills in a risk-free environment, avoiding exposure to heat, fumes, and electrical hazards. At the same time, training costs are lowered because it minimizes raw material expenses without compromising quality. This makes Seabery’s solution especially attractive for institutions and industries seeking to align welding training with ESG goals and long-term cost optimization strategies.
Seabery transforms welding training into a fully digitalized process. Every weld is measured, analyzed, and stored, generating valuable data on operator performance, learning progress, and skill gaps. This data-driven approach enables objective assessment, traceability, and informed decision-making. For both educational institutions and industrial companies, it represents a major step toward aligning welding training with Industry 4.0 and smart manufacturing strategies.
· Realistic AR-based simulation with real welding torches and accessories.
· A structured learning methodology aligned with international standards.
· Advanced analytics for objective assessment and performance tracking.
· Proven applicability in both educational institutions and industrial environments.
This approach not only accelerates skill acquisition but also supports digital transformation strategies in welding training, making it a powerful tool for organizations committed to quality, efficiency, and innovation.
Choosing the right tool for the future of welding
Choosing a welding simulator is a strategic decision that goes beyond technology. It requires alignment with training objectives, industrial relevance, learning methodology, and long-term digitalization goals.
By prioritizing Augmented Reality, data-driven evaluation, and scalable design, organizations can ensure that their investment delivers measurable results: preparing welders not just for today’s challenges, but for the future of industrial welding.